The American Red Cross First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual provides essential training for responding to emergencies‚ teaching skills to assess situations‚ provide care‚ and use life-saving devices like AEDs effectively.
1.1 Importance of First Aid and CPR in Emergency Situations
First aid and CPR are critical in emergency situations‚ providing immediate care to prevent conditions from worsening. The American Red Cross First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual emphasizes these skills to save lives‚ especially in cardiac arrest cases. Timely intervention with CPR and AED use significantly improves survival rates and recovery outcomes‚ making these techniques indispensable in emergencies.
1.2 Role of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs) in Cardiac Emergencies
AEDs play a vital role in cardiac emergencies by analyzing heart rhythms and delivering electric shocks to restore normal heartbeats. The American Red Cross First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual highlights their importance in treating sudden cardiac arrest‚ emphasizing prompt use to increase survival chances. AEDs are designed for easy operation‚ making them accessible to both trained responders and bystanders‚ thus serving as a critical lifesaving tool in emergency situations.
Basic First Aid Techniques
Basic first aid techniques include wound cleaning‚ applying dressings‚ and controlling bleeding. The American Red Cross First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual emphasizes proper assessment and the use of a first aid kit in emergencies.
2.1 Assessing the Scene and Ensuring Safety
Assessing the scene is the first step in any emergency. According to the American Red Cross First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual‚ one must ensure personal safety‚ identify hazards‚ and determine the number of casualties before providing care. This step is crucial to prevent further harm to both the responder and the victim‚ ensuring effective and safe assistance.
2.2 Primary Assessment: Airway‚ Breathing‚ and Circulation (ABCs)
The primary assessment focuses on evaluating the victim’s Airway‚ Breathing‚ and Circulation (ABCs). From the American Red Cross manual‚ this involves checking for airway obstruction‚ ensuring normal breathing patterns‚ and assessing circulation through pulse and skin color. These steps are vital to identify life-threatening conditions and provide immediate care‚ such as CPR if necessary‚ to maintain blood flow and oxygenation to vital organs.
2.3 Wound Care and Bleeding Control
Proper wound care and bleeding control are critical first aid skills. From the American Red Cross manual‚ this involves assessing the wound‚ cleaning it with sterile supplies‚ and applying direct pressure to stop bleeding. Elevating the injured limb and using tourniquets or hemostatic agents‚ if trained‚ can help control severe bleeding. Dressing the wound and monitoring for signs of infection or shock are essential steps to promote healing and prevent complications.
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
CPR is a life-saving technique combining chest compressions and rescue breaths to maintain blood circulation and oxygen supply to the brain and vital organs during cardiac arrest.
3.1 When to Perform CPR: Signs of Cardiac Arrest
CPR is crucial when a person shows signs of cardiac arrest‚ such as loss of consciousness‚ unresponsiveness‚ and absence of breathing or abnormal breathing. If a person collapses suddenly‚ is unresponsive‚ and not breathing (or only gasping)‚ begin CPR immediately. These signs indicate the heart has stopped functioning‚ and prompt intervention is vital to restore blood circulation and prevent brain damage or death. Immediate action is critical for survival.
3.2 CPR Techniques for Adults‚ Children‚ and Infants
CPR techniques vary by age group to ensure effectiveness. For adults‚ use a 30:2 chest compression-to-breath ratio‚ placing hands at the center of the chest. Children require the same ratio but with smaller chest size. Infants need a two-thumb technique‚ especially for single rescuers. Proper hand placement and depth are critical to maintain blood circulation and oxygen supply. Training ensures these methods are applied correctly in emergencies.
3.3 Hands-Only CPR vs. Standard CPR: Key Differences
Hands-Only CPR focuses solely on chest compressions without rescue breaths‚ simplifying the process for untrained bystanders. Standard CPR includes both chest compressions and rescue breaths‚ typically in a 30:2 ratio for adults and children. Hands-Only is recommended for cardiac arrest situations when a rescuer is untrained or unwilling to perform breaths‚ while Standard CPR is more comprehensive and effective when properly executed by trained individuals.
Automated External Defibrillator (AED)
An AED is a portable device that delivers an electric shock to restore heart rhythm during cardiac arrest. Proper training is essential for effective use in emergencies.
4.1 How an AED Works and Its Benefits in Emergencies
An AED analyzes a person’s heart rhythm and delivers an electric shock if a life-threatening arrhythmia is detected‚ restoring a normal heartbeat. Its benefits include rapid response‚ user-friendly design‚ and guidance through voice prompts‚ making it accessible to both trained and untrained individuals. Timely use of an AED significantly increases survival rates during cardiac emergencies‚ emphasizing its critical role in first aid and emergency care.
4.2 Step-by-Step Guide to Using an AED
Using an AED involves turning it on‚ following voice prompts‚ attaching pads to the victim’s bare chest‚ and delivering a shock if advised. Ensure no physical contact with the person during the shock. Afterward‚ continue CPR until medical help arrives. Proper pad placement and adherence to device instructions are crucial for effective use‚ as outlined in the First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual.
4.3 Maintaining and Inspecting AED Devices
Regular inspection of AED devices ensures readiness for emergencies. Check pads and battery expiration dates‚ perform monthly self-tests‚ and verify device functionality. Ensure the AED is easily accessible‚ visible‚ and in a secure location. Document inspections and maintenance activities as per guidelines in the First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual; Proper upkeep guarantees reliable operation when needed most.
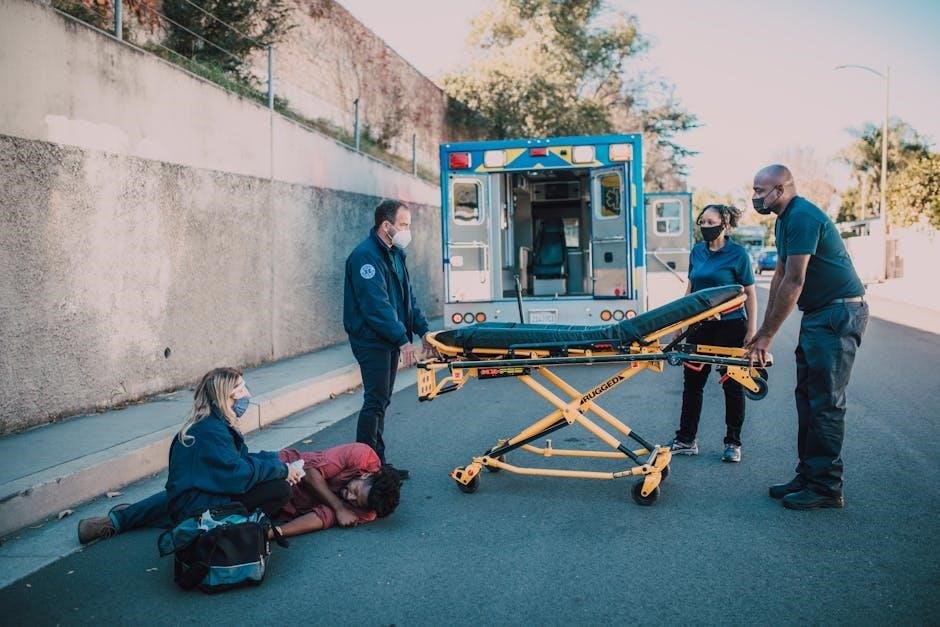
Combining First Aid‚ CPR‚ and AED in Real-Life Scenarios
Understanding how to integrate first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED use is crucial for effective emergency response. Quick assessment and prioritization of life-threatening conditions ensure timely intervention‚ saving lives in critical situations.
5.1 Responding to a Cardiac Emergency: A Step-by-Step Approach
When responding to a cardiac emergency‚ ensure the scene is safe and the person is unresponsive. Call 911 or alert others to summon help. If the person is unresponsive and not breathing‚ begin CPR. Attach an AED if available‚ following its voice prompts. Deliver shocks if advised‚ then continue CPR. Monitor the person until medical professionals arrive‚ ensuring continuous care and reassessing as needed.
5.2 Managing Choking Incidents in Adults and Children
For choking incidents‚ first ensure the person is conscious and unable to cough. For adults and children over one year‚ stand behind them and perform abdominal thrusts. For infants‚ use chest thrusts. If the person becomes unresponsive‚ begin CPR. Always call for emergency medical help and follow the steps outlined in the First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual to ensure proper technique and safety.
5.3 First Aid for Burns‚ Injuries‚ and Other Common Accidents
For burns‚ cool the affected area with cool water‚ avoid ice‚ and cover with a non-stick dressing. Stop bleeding by applying direct pressure and elevating the injury. For fractures‚ immobilize and seek medical help. The First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual emphasizes immediate care to prevent further harm and promote recovery‚ ensuring timely and effective responses to common accidents.
Legal and Ethical Considerations in First Aid and CPR
Understanding legal protections‚ ethical practices‚ and confidentiality is crucial for first responders. The First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual emphasizes balancing care with respect for privacy and consent.
6.1 Good Samaritan Laws and Liability Protection
Good Samaritan laws protect individuals who provide first aid in emergencies from legal liability‚ ensuring they act in good faith without gross negligence. These laws vary by location but generally shield responders from civil lawsuits‚ encouraging bystanders to assist without fear of legal repercussions. The First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual highlights the importance of understanding these protections to confidently administer care during critical situations.
6.2 Confidentiality and Ethical Practices in Emergency Care
Confidentiality and ethical practices are crucial in emergency care. First responders must protect patient privacy‚ adhering to laws like HIPAA‚ and avoid sharing personal health information without consent; Ethical guidelines emphasize respect‚ dignity‚ and consent‚ ensuring care is provided compassionately and without discrimination. The Participants Manual underscores these principles‚ guiding responders to uphold trust and professionalism while delivering emergency aid responsibly.
Skill Retention and Practice
Regular training and practice are vital for maintaining proficiency in first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED use. The Participants Manual emphasizes continuous learning and skill refreshers to ensure readiness in emergencies.
7.1 Importance of Regular Training and Refreshers
Regular training and refreshers are crucial for maintaining first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED skills. The Participants Manual highlights that periodic updates ensure knowledge stays current with medical advancements and best practices‚ reducing errors in emergencies. Continuous learning reinforces muscle memory‚ builds confidence‚ and prepares individuals to act decisively. Without regular practice‚ skills can fade‚ compromising the ability to provide effective care during critical situations.
7.2 Using Manuals and Resources for Continuous Learning
The First Aid/CPR/AED Participants Manual serves as a vital resource for continuous learning‚ offering detailed guidelines and visual aids to reinforce training. Supplementary materials‚ such as skill sheets and online modules‚ provide additional support. Regular review of these resources helps participants retain knowledge and stay updated on the latest techniques‚ ensuring preparedness for real-life emergencies and enhancing their ability to deliver effective care confidently.
Emergency Preparedness and Response Plans
Developing a comprehensive emergency action plan ensures readiness for crises‚ including first aid kit essentials and clear response protocols to address various incidents effectively and efficiently.
8.1 Creating a First Aid Kit and Essential Supplies
A well-stocked first aid kit is crucial for emergency preparedness. It should include bandages‚ antiseptic wipes‚ gloves‚ a CPR mask‚ and over-the-counter medications. Regularly inspect and restock supplies to ensure readiness. Customize kits for specific settings‚ such as workplaces or homes‚ and include an AED for cardiac emergencies. Proper organization and easy access are key to effective response during critical situations.
8.2 Developing an Emergency Action Plan for Workplaces and Homes
A comprehensive emergency action plan ensures preparedness for crises like injuries or cardiac arrests. Identify potential risks‚ establish escape routes‚ and designate assembly points. Include communication strategies and first aid procedures. Regular drills and updates keep the plan effective. Tailor plans for workplaces and homes‚ ensuring all members understand their roles. A clear‚ well-rehearsed plan enhances safety and minimizes response time during emergencies.

Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Real-life scenarios demonstrate the lifesaving impact of first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED training‚ showcasing how immediate action during cardiac arrests and injuries leads to successful outcomes and inspired learning for future emergencies.
9.1 Successful Outcomes of Timely CPR and AED Use
Timely CPR and AED use have proven critical in saving lives during cardiac emergencies. For instance‚ a person experiencing sudden cardiac arrest was revived after a bystander performed CPR and applied an AED‚ restoring a normal heart rhythm before medical help arrived. Such real-world examples highlight the importance of immediate intervention and demonstrate how proper training leads to positive outcomes‚ inspiring others to learn these lifesaving skills. These cases underscore the value of first aid education in emergencies.
9.2 Lessons Learned from Emergency Response Scenarios
Emergency response scenarios highlight the importance of preparation and quick thinking. For example‚ a choking incident demonstrated the effectiveness of back slaps and abdominal thrusts‚ while a burn case emphasized immediate cooling to prevent further damage. These experiences underscore the value of adhering to first aid protocols and the need for regular training to stay prepared for unexpected situations‚ ultimately improving outcomes and saving lives in critical moments.
Proper first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED training empowers individuals to act confidently in emergencies‚ potentially saving lives. The American Red Cross Manual serves as a vital resource‚ ensuring preparedness and competence in critical situations.
10.1 The Impact of Proper Training on Saving Lives
Proper first aid‚ CPR‚ and AED training significantly enhances the ability to respond effectively in emergencies. The American Red Cross Participants Manual emphasizes that timely interventions can prevent fatalities‚ reduce injury severity‚ and improve outcomes. Equipping individuals with these skills fosters confidence and preparedness‚ ultimately saving countless lives in critical situations. The manual’s structured approach ensures that learners are well-prepared to act decisively when emergencies arise.
10.2 Encouraging Others to Learn First Aid and CPR
Advocating for widespread first aid and CPR training can significantly enhance community safety. The American Red Cross Participants Manual highlights the importance of empowering others with life-saving skills. By sharing knowledge and experiences‚ individuals can inspire friends‚ family‚ and colleagues to enroll in training programs. This collective effort creates a network of prepared individuals capable of responding effectively during emergencies‚ fostering a safer and more resilient community for everyone.
